CO2M
Copernicus Anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide Monitoring

Mission
First mission to measure the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere by human activity
Satellites / Instruments
Sentinel 7A and Sentinel 7B satellites (in 2025) carrying CO2I, MAP and CLIM instruments
Skills
Simulation of the telemetry of the 3 CO2M instruments (CO2I, MAP, CLIM), L0 product generation and geometry module
Date
From 2020 to today
The CO2M project
The amount of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere is approaching a level that humans may never have experienced before. The Copernicus Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Mission (CO2M) is now more than ever needed.
This is the first mission to measure the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere by human activity. The data collected by CO2M will be used to help monitor and implement the targets set in the Paris Agreement.

Illustration du satellite / © ESA
The CO2M mission includes the launch of two identical satellites (Sentinel 7A and 7B) by the end of 2025.
In addition, CO2M follows the Sentinel missions of the EU’s Copernicus environmental monitoring programme. This programme is the largest provider of Earth observation data in the world.
For more information, see the ESA article and its website for CO2M.
![]()
The objectives
- Development of prototype ground segment modules: simulation of the telemetry of the 3 instruments (CO2I, MAP, CLIM)
- Generation of L0 products and geometry module for the generation of level 1 products
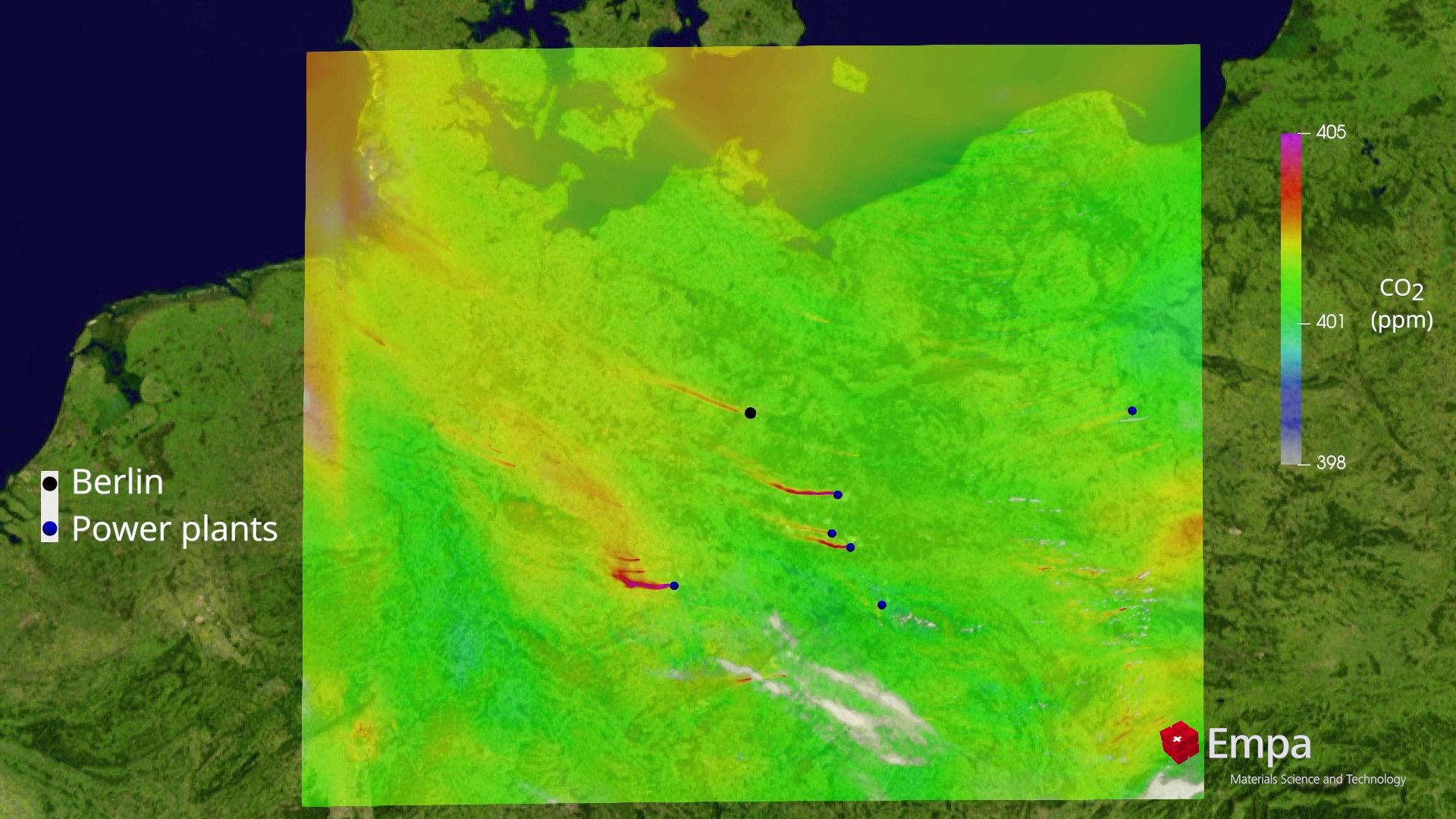
Simulated data showing carbon dioxide plumes / © ESA
Consortium
ESA, EUMETSAT, OHB, Thales
Key words
observation, satellite, earth, studies, carbon dioxide, CO2, activity, human, copernicus, sentinel, atmosphere, climate
SCIENCE FOR EARTH CARE
The Earth Observation Unit of Magellium is an expert in optical space missions and geophysical and biophysical applications. The EO unit provides high level of expertise and full capacity on the whole processing chain, enabling it to respond to all projects from the greatest space orders such as ESA and CNES.

