GRACEFUL
GRavimetry, mAgnetism and CorE FLow
Collaboration between Royal Observatory of Belgium (Véronique Dehant), CNES (Mioara Mandea) and LEGOS (Anny Cazenave)

Mission
Detecting dynamic processes from the Earth’s core using a synergy of satellite observations
Satellites / Instruments
Satellite observations of the magnetic field (CHAMP, SWARM), gravity (GRACE, GRACE FO) and the Earth’s rotation (IERS)
Skills
Processing and analysis of satellite measurements
Modelling of geophysical processes from the earth’s surface to its deep interior
Multidisciplinarity – synergy
Basic research
Date
From 2020 to today
The GRACEFUL project
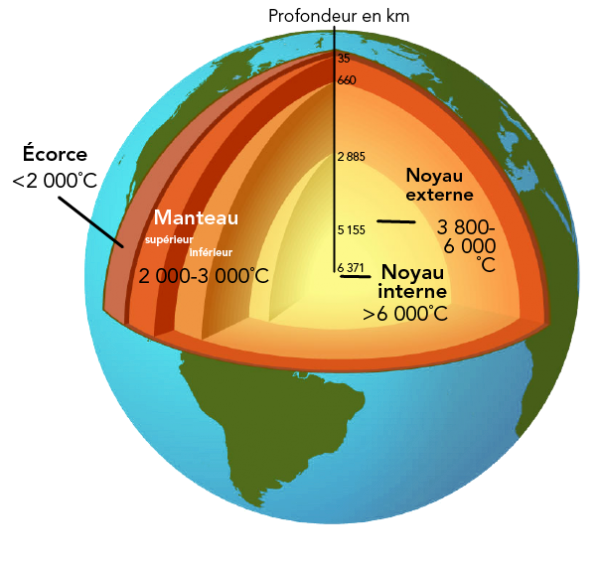
The GRACEFUL project aims to better understand the internal dynamics of our planet, in particular the Earth’s core. The Earth is made up of a solid metallic core (the inner core), a fluid metallic envelope (the outer core) within which the Earth’s magnetic field is generated by a dynamo effect, a solid envelope made up mainly of silicates (the mantle) and the Earth’s crust (the lithosphere) on which we stand. The atmosphere, ocean, hydrosphere and cryosphere are the Earth’s fluid outer shells.
As the Earth’s core is located several thousand kilometres below our feet, it is not directly accessible to us. Knowledge of its existence is based on indirect evidence, mainly from seismology, which uses the principle of wave propagation inside a body to produce an “ultrasound” of the Earth’s interior. However, seismology only allows us to obtain a fixed image of the Earth’s interior and does not allow us to study its internal dynamics. This ambitious project aims to use satellite observations of the Earth’s magnetic field, gravity and rotation to better understand the movement of metallic fluid within the outer core and its interactions with the inner core and mantle.
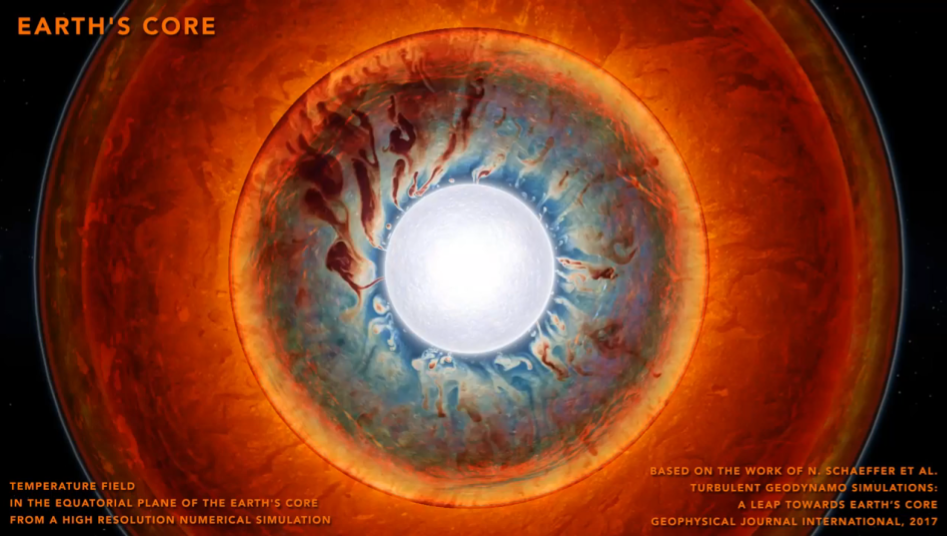
Temperature field in the equatorial plane of the Earth’s core from a high resolution numerical simulation
After Schaeffer et al., 2017, GJI
The GRACEFUL (GRavimetry, mAgnetism, rotation and CorE Flow) project is a Synergy project (number 855677) of the European Research Council (ERC) in the framework of the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme. It is led by Véronique Dehant (Royal Observatory of Belgium), Mioara Mandea (CNES) and Anny Cazenave (LEGOS).
Visit the official GRACEFUL project website here.
![]()
The role of the unit in GRACEFUL
Magellium’s Earth Observation Unit is responsible for the processing and analysis of space gravity data acquired by the GRACE (Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment) and GRACE Follow-On missions. The GRACE and GRACE-FO data are then corrected for all surface processes (ice melt, oceanic and atmospheric circulation, water cycle, earthquakes, glacial isostatic adjustment) in order to isolate variations in the gravity field from the deep Earth. These data are then compared with models of the Earth’s interior developed by our partners at the Royal Observatory of Belgium and the IsTerre Institute in Grenoble.
Key partners
CNES, LEGOS, Royal Observatory of Belgium
Key words
observation, satellite, Earth, studies, altimetry, gravimetry, Earth field, gravity, rotation, magnetism, Earth core, CNES, Belgium, LEGOS
SCIENCE FOR EARTH CARE
The Earth Observation Unit of Magellium is an expert in optical space missions and geophysical and biophysical applications. The EO unit provides high level of expertise and full capacity on the whole processing chain, enabling it to respond to all projects from the greatest space orders such as ESA and CNES.

