Moheacan
Monitoring ocean heat content (OHC) and Earth energy imbalance (EEI) from space observations

Mission
Global Ocean Heat Content (OHC) and Earth Energy Imbalance (EEI) monitoring
Instruments
GRACE
Skills
Altimetry and gravity data
Date
From 2019 to today
The MOHeaCAN project
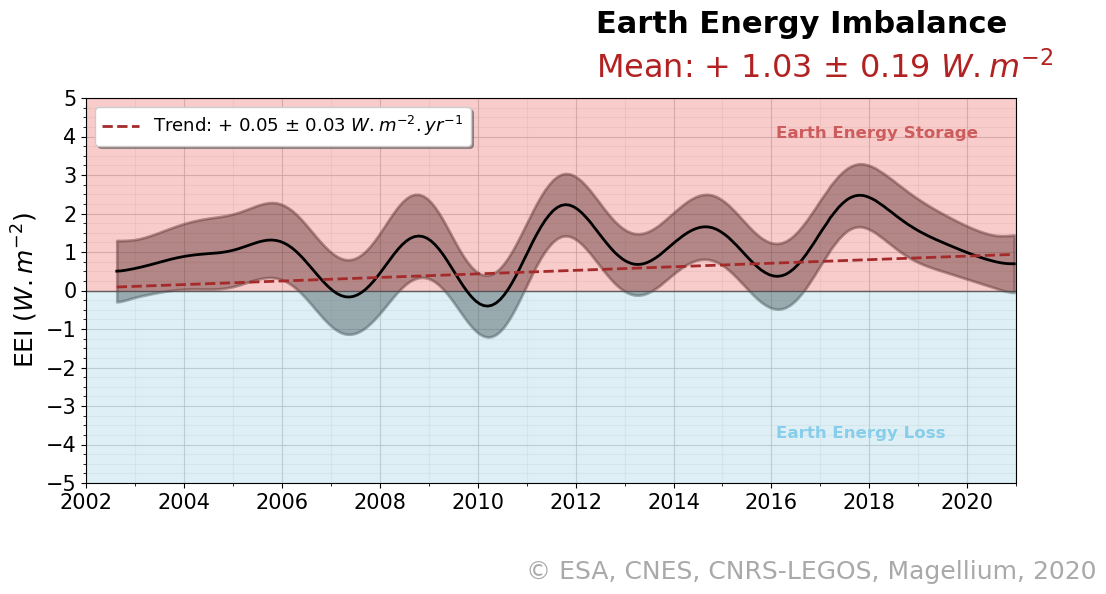
Since the industrial era, emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) into the atmosphere due to human activities have reduced the amount of infrared energy that the Earth emits into space. Today, the Earth emits less energy into space than it receives from the sun. As a result, there is an Earth Energy Imbalance (EEI).
Because of this IEE, the climate system stores energy, mainly in the form of heat. This excess energy disrupts many things, including the global hydro-energy cycle, and creates what is known as climate change. Excess energy heats the oceans, causing sea levels to rise and sea ice to melt. It melts the land ice, also causing sea level rise. It causes a rise in surface temperatures, altering the hydrological cycle and producing droughts and floods.
Therefore, estimating and analysing the IEE is essential to understanding the Earth’s changing climate.
![]()
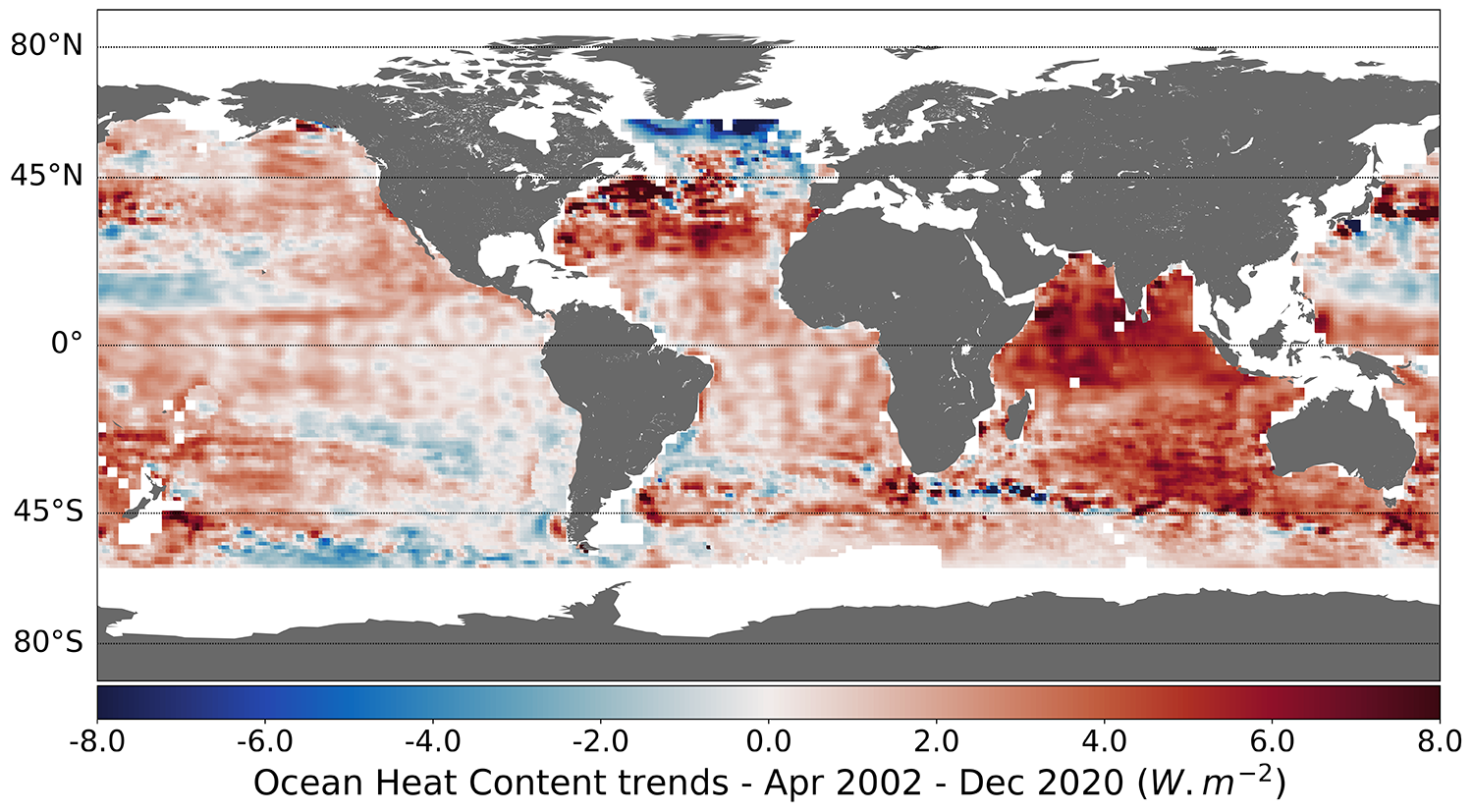
Heat content of the oceans
The MOHeaCAN (Monitoring Ocean Heat Content and earth energy imbalANce) project is an ESA-supported project led by the Magellium Earth Observation Unit with scientific experts from LEGOS.
Thanks to the support of CNES, estimates of GOHC (Global Ocean Heat Content) and IEE are further improved and available on the ODATIS/AVISO portal.
In parallel, the CNRS is funding the evaluation of the IEE against other estimates, based on space and/or in situ observations.
Find more information on the MOHeaCAN website project.
The objectives of MOHeaCAN
-
-
- Calculate global ocean heat content (GOHC) and Earth energy imbalance (EEI) from space geodetic data
-
-
-
- Provide the possibility to extend heat content monitoring for future applications and solutions
-
Key words
ESA, Centre National Océanographique, LOPS, Mercator Ocean, Met Office, LEGOS, CNES, CNRS, Barcelona Supercomputing Center
Key words
observation, satellite, earth, studies, OHC, ocean heat content, EEI, earth energy imbalance, climate, altimetry, gravity, in-situ data, geodetic data
SCIENCE FOR EARTH CARE
The Earth Observation Unit of Magellium is an expert in optical space missions and geophysical and biophysical applications. The EO unit provides high level of expertise and full capacity on the whole processing chain, enabling it to respond to all projects from the greatest space orders such as ESA and CNES.

