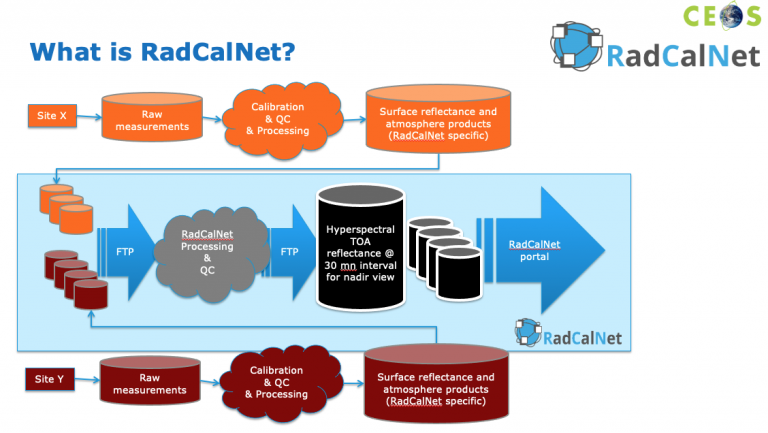
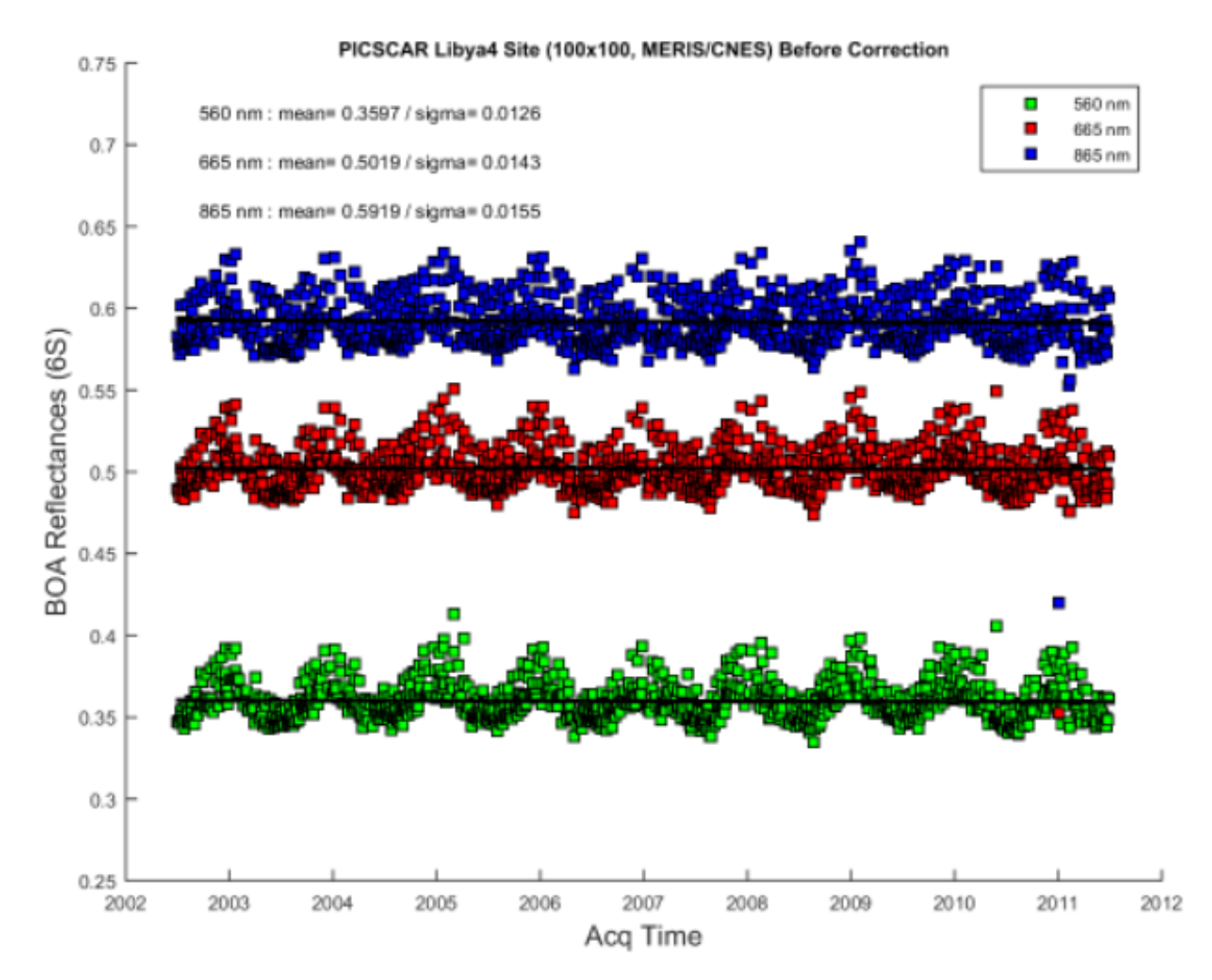
Smoke detection
Smoke detection
Mission
Smoke detection after a fire and analysis of the impact on agriculture
Skills
Algorithm development, studies
Date
From 2020 to 2021
The work on smoke detection
The smoke emitted by fires, even thousands of kilometres from the source, can have a significant impact on the surrounding vegetation. This is particularly the case for vineyards, as the vinasse produced by smoke-affected grapes will have a strongly modified taste.
Fortunately, the Copernicus Atmospheric Monitoring Service (CAMS) provides a large amount of atmospheric data extracted from various physical models, satellite data and in situ observations.
The specific CAMS data indicate the location of smoke at any given time from a selected fire, both at ground level and at several heights above the ground. A first study by the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) showed that the specific CAMS data are difficult to use to determine the affected vineyards.

The unit’s work consists of extending this proof-of-concept study by developing automatic tools to easily retrieve data stored in CAMSAPI, visualise it, extract localised data and test this methodology on a large number of people.
![]()
The objectives of the smoke detection
-
-
- Automatic recovery of CAMS data
- Smoke impact index
- Data visualization
- QGIS plugin
- Comparison with S5P and IASI acquisitions
-
Key partners
CNES, SPASCIA
Key words
observation, satellite, earth, studies, smoke, detection, copernicus, vineyard, agriculture, impact
SCIENCE FOR EARTH CARE
The Earth Observation Unit of Magellium is an expert in optical space missions and geophysical and biophysical applications. The EO unit provides high level of expertise and full capacity on the whole processing chain, enabling it to respond to all projects from the greatest space orders such as ESA and CNES.